inside the blink of a watch, artificial intelligence (AI) has leaped from the pages of technological know-how fiction into our everyday lives. From when you ask Alexa for the weather forecast to when you unlock your iPhone with Face ID, you interact with AI. but what precisely is this generation that is reshaping our global? let’s dive into the charming realm of AI and discover everything you want to know. What is artificial intelligence (AI)? Everything you need to know.
A Brief History of AI: From Dreams to Reality
The concept of artificial intelligence isn’t new—it is been dancing in our imaginations for hundreds of years. Ancient myths pointed out mechanical men, at the same time as sci-fi novelists dreamed up robotic companions. But it wasn’t until the Fifties that AI started out its adventure from fiction to reality.
In 1950, British mathematician Alan Turing posed a groundbreaking query: “Can machines count on?” His well-known Turing check challenged laptop systems to idiot people into believing they had been chatting with each other character. Six years later, at a Dartmouth College workshop, laptop scientist John McCarthy coined the period “artificial intelligence.” AI changed into born!
“What we want is a machine that can learn from experience.” – Alan Turing
but AI’s direction hasn’t been all uphill. it’s far faced “AI winters”—periods at the same time as improvement slowed and funding dried up. Then got here “AI springs,” whilst breakthroughs like IBM’s Deep Blue beating world chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997 reignited pleasure. today, we are in an AI summertime, with advancements like OpenAI’s ChatGPT making headlines.
How Does AI Work? Demystifying the Magic
At its center, AI is set creating machines that can assume, learn, and make decisions. However, how does it pull off this magic? it all boils down to four key components:
- Data: Just as we learn from experiences, AI learns from data. Massive amounts of it. Whether it’s images for facial recognition or text for language models, data is AI’s lifeblood.
- Algorithms: These are AI’s decision-making rules. They tell the system how to process data, find patterns, and make choices.
- Training: AI doesn’t get it right the first time. Through training, it learns from examples. Show a model thousands of cat pictures, and it’ll learn to spot cats.
- Inference: Once trained, AI applies its knowledge to new data. Given a fresh image, it can infer, “Yes, that’s a cat!”
Types of Artificial Intelligence: Weak AI vs. Strong AI
Not all AI is created equal. Some systems are one-trick ponies, while others aspire to match human intellect. What is artificial intelligence (AI)? Everything you need to know.
Strong AI vs. Weak AI: Brains or Just Good at Chess?
- Weak AI (Narrow AI): These are specialists. They excel at specific tasks but can not venture past their education. Think of Spotify’s music hints or AlphaGo’s mastery of the game Go. They’re pretty top at one issue however clueless approximately everything else.
- Strong AI (Artificial General Intelligence): This is the holy grail—AI that matches or surpasses human-level smarts across the board. It would understand context, learn any task, and maybe even have consciousness. We’re not there yet, but it’s the ultimate goal.
What Are the 4 Types of Artificial Intelligence?
AI’s capabilities fall into four categories, each more advanced than the last:
- Reactive Machines: The most basic type. They react to current situations without memory of the past. IBM’s Deep Blue, which beat Kasparov, was reactive. It saw the chessboard’s current state and chose the best move, but it couldn’t learn from previous games.
- Limited Memory: These AI systems use past data to make better decisions. Your Tesla’s Autopilot remembers the speed and location of nearby cars to make safer choices.
- Theory of Mind: We’re entering sci-fi territory. This AI would understand that humans (and other AI) have thoughts, feelings, and intentions that shape behavior. It’s crucial for truly interactive AI, like future elder care robots.
- Self-Awareness: The pinnacle. This AI would have consciousness, self-awareness, and perhaps even feelings. We’re in philosophical territory: What makes us “us”? This type is purely theoretical for now.
AI for Everyone: It’s Not Just for Tech Gurus
Think AI is only for Silicon Valley types? Think again! It’s already woven into your daily life:
- Smartphones: Ever used Google Lens to pick out a plant or translate a menu? That’s AI at paintings.
- Smart Home: Alexa and Google Home use natural language processing (NLP) to understand your commands.
- Apps: From Grammarly solving your typos to Snapchat’s face filters, AI is making apps smarter.
“AI is the new strength.” – Andrew Ng, AI pioneer
Differences Between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning
These terms often get tossed around like synonyms, but they’re more like nesting dolls:
- AI is the biggest doll, representing any technique that enables machines to mimic human intelligence.
- Inside that, Machine Learning (ML) is an AI method where systems learn from data without being explicitly programmed. They find patterns on their own.
- Nestled within ML is Deep Learning (DL). Inspired by our brain’s structure, it uses artificial neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”) to learn complex patterns.
Deep Learning vs. Machine Learning: The Brain-Inspired Tech
- Machine Learning finds patterns in structured data. Give it spreadsheets of housing prices, and it’ll predict future prices.
- Deep Learning shines with unstructured data like images or speech. By mimicking brain networks, it can grasp abstract concepts. That’s how it masters tasks like recognizing faces or translating languages. What is artificial intelligence (AI)? Everything you need to know.
| Aspect | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Structured | Unstructured (images, text) |
| Feature Extraction | Manual | Automatic |
| Hardware Needs | Lower | Higher (GPUs) |
| Training Data | Less | Much more |
| Interpretability | Higher | Lower (“black box”) |
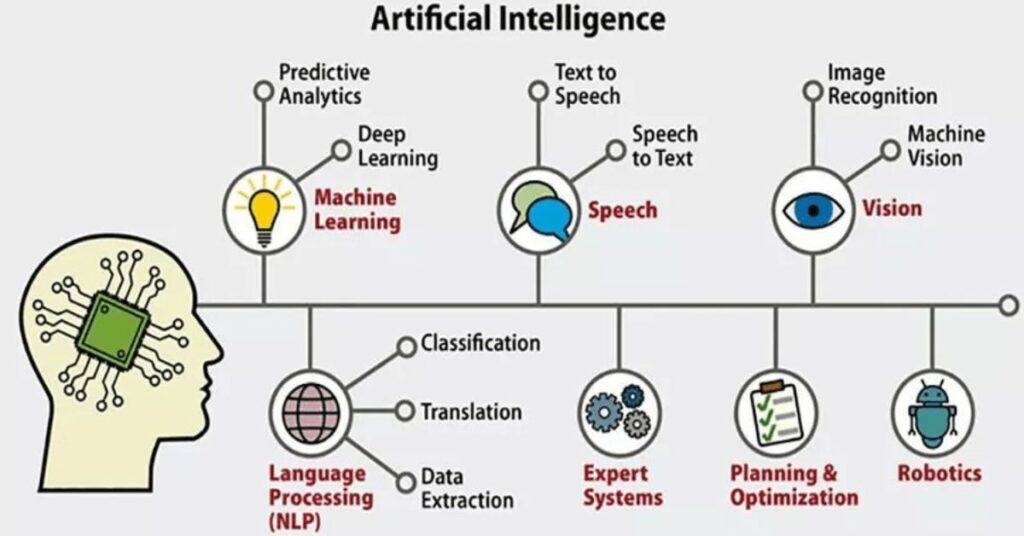
What Are Examples of AI Technology and How Is It Used Today?
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): This facilitates machines recognize, interpret, and generate human language. It powers the entirety of Siri’s responses to Google Translate’s accuracy.
- Computer Vision: AI that translates visible information. It’s why your iPhone’s Face ID works even with a brand-new haircut and the way radiologists use AI to identify tumors in X-rays.
- Robotics: AI guides robots in complex tasks. In factories, they work alongside humans, handling dangerous or repetitive jobs. In hospitals, AI-driven robots assist in delicate surgeries.
Applications of AI: From Healthcare to Hollywood
AI’s versatility is staggering:
- Healthcare: AI does not just spot sicknesses; it predicts them. fashions examine genetics, way of life, and clinical history to flag excessive-chance sufferers. within the lab, AI accelerates drug discovery using predicting which compounds will paint.
- Finance: AI is your financial guardian. It detects fraudulent credit card swipes in milliseconds. Robo-advisors like Wealthfront use AI to provide customized funding recommendations at a fragment of human expenses.
- Entertainment: Ever wondered how Netflix knows you’ll love that indie film? AI analyzes your viewing history, ratings, and even the time you watch to suggest perfect matches.
The Rise of Generative Models: AI Gets Creative
We’ve entered an era where AI doesn’t just analyze; it creates:
- AI-Generated Art: Tools like DALL-E and Midjourney turn text into stunning images. Type “cosmic ballet in Van Gogh style,” and voilà—a masterpiece is born.
- AI Music: OpenAI’s Jukebox composes original songs in any genre. It’s not topping charts yet, but the potential is striking.
Introduction to Generative AI: The Next Big Thing
Generative AI is like having a creative partner. You provide a prompt, and it generates original content—text, images, code, you name it.
- GPT Models: OpenAI’s GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) series, including the famous ChatGPT, can write articles, stories, and even computer programs. They understand context so well that their outputs often feel human-crafted.
“Generative AI is democratizing creativity.” – Demis Hassabis, DeepMind CEO
AI in the Workforce: Your New Coworker
AI entering the job market stirs both excitement and anxiety. Will robots take our jobs? The reality is nuanced:
- Job Automation: Yes, AI will automate tasks. Oxford University predicts 47% of U.S. jobs are at risk. But often, it’s specific tasks within a job, not the entire role.
- AI-Human Collaboration: The future is teamwork. In law firms, AI sifts through thousands of cases, then lawyers use those insights to build stronger arguments.
- Upskilling: As AI handles routine tasks, human roles will evolve. McKinsey suggests we’ll spend 60% more time using technological skills. Continuous learning is key.
What is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)?
Remember the smart, adaptable AI from movies? That’s AGI—artificial intelligence that matches human versatility. It would understand context, learn any task, and navigate our complex world.
- Common Sense: Toddlers know a cup can hold water. AI needs to be explicitly taught such basic facts.
- Creativity: AI can mimic art styles, but can it innovate new ones?
- Abstract Reasoning: We easily grasp metaphors. AGI needs this skill to truly think like us.
When will we achieve AGI? Opinions vary wildly:
- Ray Kurzweil (Google): By 2029
- Yann LeCun (Meta AI): Maybe not in our lifetime
Why is Artificial Intelligence Important?
AI isn’t just cool tech; it’s a tool for tackling humanity’s biggest challenges:
- Climate Change: AI models predict climate patterns, optimize renewable energy grids, or even seize carbon greater correctly.
- Disease: During COVID-19, AI rapidly screened drug compounds, speedy-monitoring vaccine development.
- Productivity: AI handles mundane tasks, freeing us for creative work. It’s estimated to boost productivity by 40% by 2035.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| 24/7 Operation | Job Displacement |
| Unbiased Decisions* | AI Bias* |
| Handles Big Data | Data Privacy Issues |
| Reduces Human Error | Lacks Common Sense |
| Personalization | Over-Dependence |
A Guide to Artificial Intelligence in the Enterprise
For businesses, AI isn’t a luxury; it’s survival. But integrating AI takes more than just buying software. What is artificial intelligence (AI)? Everything you need to know.
- Identify Use Cases: Where could AI boost efficiency? Maybe in customer service or supply chain optimization.
- Data Strategy: AI is only as good as its data. Audit your data for quality and bias.
- Choose Tools: From IBM Watson to Google Cloud AI, match tools to your needs.
- Upskill Staff: Offer AI training to foster a tech-savvy culture.
- Start Small: Pilot AI in one department, then scale up.
“every business enterprise is a records company, even though they do not know it yet.” – Mark Cuban
Augmented Intelligence vs. Artificial Intelligence
Here’s a key idea: AI’s not replacing us; it’s empowering us. That’s augmented intelligence—AI as a partner that enhances our capabilities.
- In healthcare, IBM Watson doesn’t replace doctors. It rapidly analyzes patient data, research papers, and clinical trials, and then suggests treatment plans. The doctor makes the final, augmented decision.
- Salesforce Einstein doesn’t automate sales. It predicts which leads are most promising, so reps focus their human skills—empathy, persuasion—where they’ll count most.
Ethical Use of Artificial Intelligence
As AI’s have an impact on growth, so do ethical issues:
- AI Bias: In 2015, Amazon scrapped an AI hiring device that penalized resumes containing the phrase “ladies.” Why? It becomes trained on past resumes, broadly speaking from guys.
- Privacy: Your data trains AI. But how much do they know? With every “Alexa, order paper towels,” you’re sharing habits and preferences.
- Transparency: Many AI systems are “black boxes.” They make decisions, but even their creators don’t always know why. That’s troubling when those decisions affect loans, jail sentences, or medical treatments.
AI Governance and Regulations
The AI genie is out of the bottle, making rules crucial:
EU’s AI Act: Proposed in 2021, it’s the world’s first complete AI law. It classifies AI structures by using hazard stage, banning “unacceptable hazard” applications like social scoring.
U.S. Approach: More region-precise. The FDA regulates AI in medical gadgets, whilst the NHTSA oversees self-driving vehicles.
IEEE Ethically Aligned Design: An international preferred to ensure AI respects human rights and well-being.
“With great power comes great responsibility.” – Stan Lee (fitting for AI, too!)
As we look ahead, global collaboration on AI governance is key. Just as the internet needed unified standards, AI’s borderless nature demands a worldwide ethical framework. What is artificial intelligence (AI)? Everything you need to know.
FAQs
A: Artificial intelligence is the ability of machines to exhibit intelligent behavior, learn from experience, and perform human-like tasks.
A: Traditional programming requires explicit instructions, while AI can learn from data and find solutions without being explicitly programmed.
A: The main types are narrow/weak AI, general/strong AI, and superintelligence. Narrow AI focuses on specific tasks while general AI can perform any task.
A: Today’s AI is still narrow – it cannot match human flexibility and general problem-solving abilities. However, it can perform some tasks faster or more accurately than people.
A: Common applications are digital assistants, medical diagnostics, predictive analytics, automated vehicles, facial recognition, and more. AI is increasingly being used across industries like healthcare, education, transportation, and more.
A: While some jobs are at risk of automation, AI is also expected to create new types of jobs and roles that don’t yet exist. The impact will depend on how individual industries adapt.






